Spring Boot 介绍
Spring Boot 目标是减少 Spring 应用程序的配置。
自动依赖管理
parent
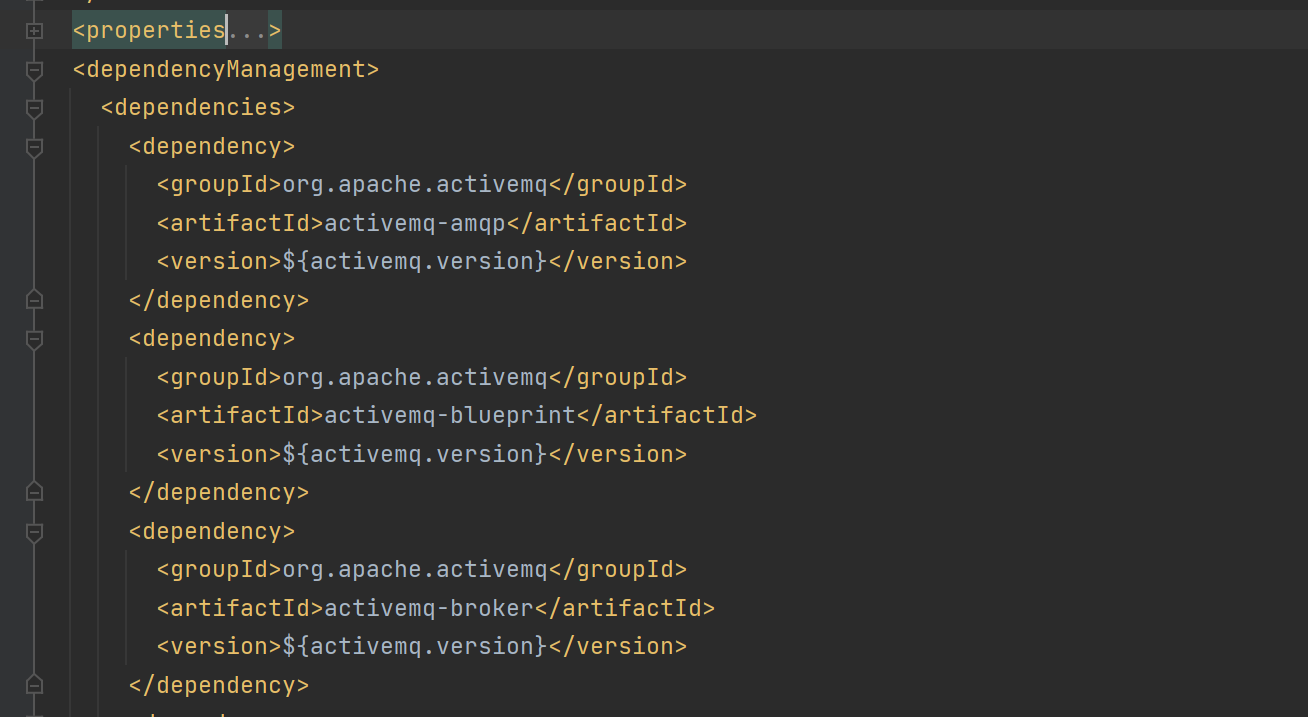
Spring Boot 所做的自动依赖管理,是由于在 Maven pom 配置文件中继承了 Spring Boot 的配置文件 spring-boot-parent,spring-boot-parent 有继承了 spring-boot-dependencies(本质上来说,就是在本地 pom 文件中引入了 spring-boot-dependencies,进行依赖管理避免依赖冲突)。
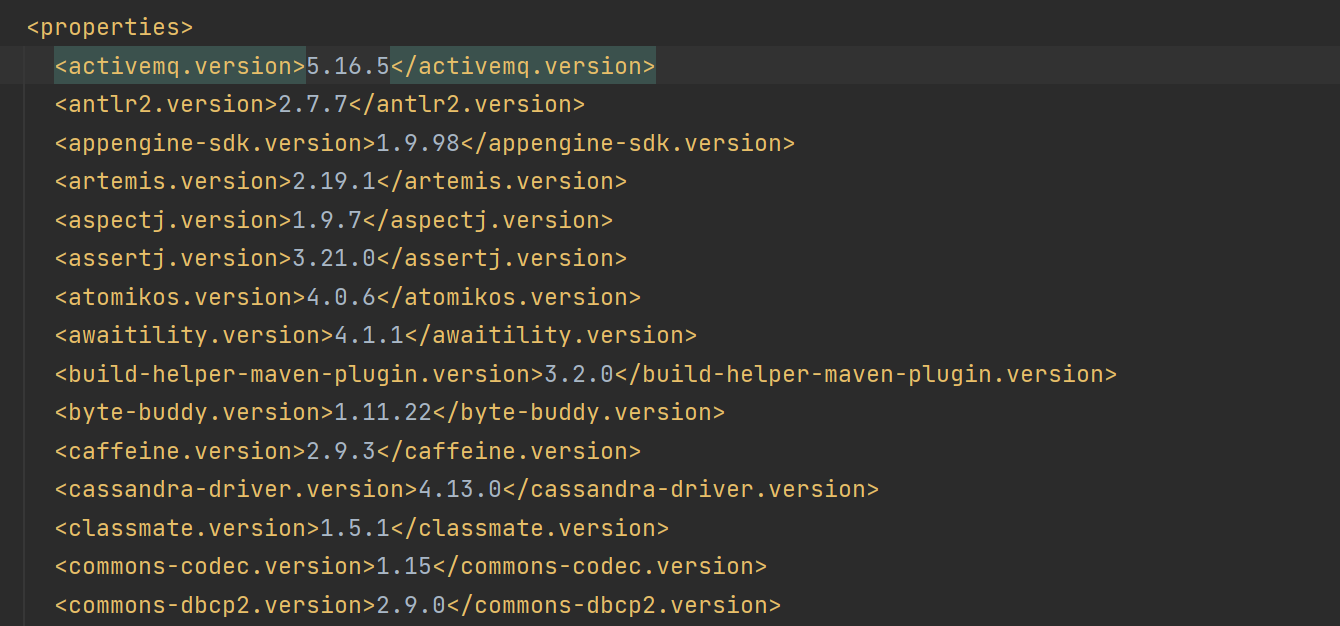
spring-boot-dependencies 中定义了依赖信息和版本信息。具体来说,是利用 properties 定义了版本信息,利用 dependencyManagement 定义依赖管理。
利用阿里云场景 Spring Boot 工程,使用的是引入 spring-boot-dependencies 的方式。
starter
starter 定义了当前项目所使用的依赖坐标,减少依赖配置。starter 在 Spring Boot 中的命名规范为 spring-boot-starter-xxx 或者 xxx-spring-boot-starter(第三方技术)。
在本地 pom 配置文件中导入 starter 依赖,就可以直接使用了。
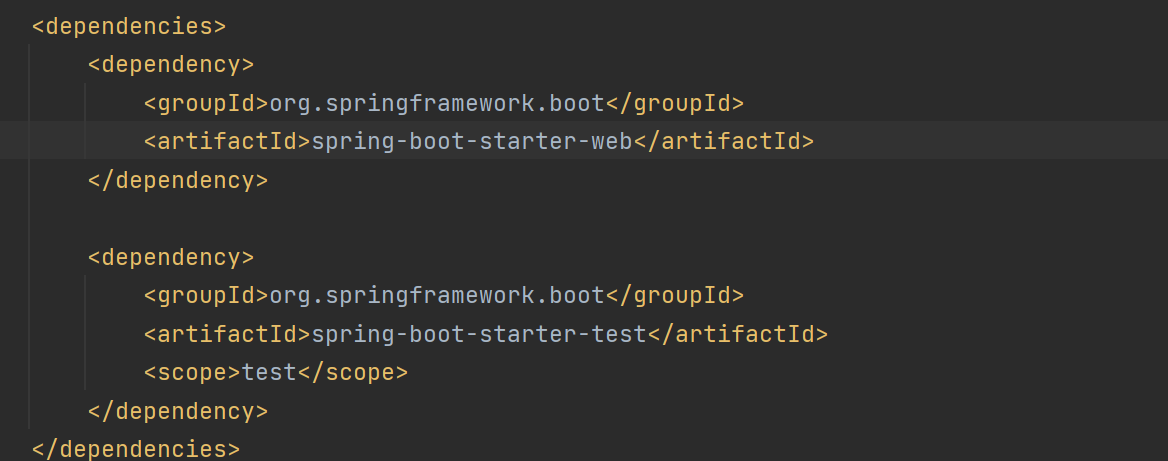
在引入 spring-boot-starter-web 时,运行程序会自动启动 tomcat 服务器(内嵌 tomcat 服务器),这是因为 spring-boot-starter-web 引用了 spring-boot-starter-tomcat。
内嵌 tomcat 服务器的原理就是,将 tomcat 服务器作为对象,在 Spring IOC 容器中管理起来。
配置文件
Spring Boot 的默认配置文件为 application.properties,同时 Boot 支持三种配置文件格式:
- properties
- yml
- yaml
优先级 properties > yml > yaml
可以在命令行参数中指定以下参数,来修改配置文件名:
- –spring.config.name 参数,指定配置文件名(不包括扩展名)。
- –spring.config.location 参数,指定配置文件全路径名。
配置文件位置
Spring boot 按照以下顺序读取配置文件,后面的配置会覆盖前面的配置。
- classpath(开发时)
- classpath 根路径。
- classpath 下的
/config包。
- jar 当前目录(运行时):
- 当前目录下。
- 当前目录下的
config/子目录。 config/子目录的直接子目录。
外部化配置
Spring Boot 支持外部化配置,可以使用各种外部配置源,包括Java properties 文件、YAML文件、环境变量和命令行参数。
读取配置信息
配置的属性值可以通过以下方式读取值:
- @Value 注入到 Bean 中。
- 可以通过 Spring 的 Environment 访问(定义一个 Environment 类型的属性,使用 @Autowired 自动装配)。
- 通过 @ConfigurationProperties 绑定对象(首先得将对象定义为 Spring Bean),或者 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解。
1 |
|
使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解读取配置时,支持配置属性的宽松绑定(支持中划线、下划线、不区分大小写),前缀 prefix 命名规范仅仅支持小写字母、中划线、数字。
在 Maven 中引入 JSR303 及其实现类(如 Hibernate),使用 @Validated 注解开启数据校验功能,在字段上使用 @MAX、@MIN、@Email 等注解进行数据校验。
外部配置源顺序
Spring Boot 使用以下外部配置源的顺序,后面的配置会覆盖前面的配置:
- 默认属性(通过 SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties 指定)。
- @Configuration 类上的 @PropertySource 注解(这样的属性源直到 spring 容器启动时才会被加载,但是对于配置某些属性来说已经太晚了,如 logging 配置)。
- 配置文件,如 application.properties。
- RandomValuePropertySource
- 环境变量。
- Java System properties,使用 System.setProperties() 指定。
java:comp/env中的 JNDI 属性。ServletContextinit parameters.ServletConfiginit parameters.- 来自 SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON 的属性(嵌入环境变量或系统属性中的内联 JSON)。
- 命令行参数,使用
--属性名=值指定。 - 在测试中的 properties 和 args 属性, @SpringBootTest 注解指定
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"server.port=8080", ...}, args={"--server.port=8081", ...}),其中 args 属性比 properties 属性优先级高。 - 在测试中的 @DynamicPropertySource 注解。
- 测试中的 @TestPropertySource 注解.
- 当 devtools 处于活动状态时,
$HOME/.config/spring-boot目录下的Devtools全局设置属性。
多环境配置
Spring Boot 的多环境配置,可以在单个配置文件中指定,也可以在多个配置文件中指定,每一个环境对应一个配置文件(推荐)。
单文件配置
在同一个配置文件中可以指定多个环境的配置,环境之间使用 --- 分隔,环境名称使用 spring.profiles 或者 spring.config.activate.on-profile 指定,使用的环境使用 spring.profiles.active 指定。
1 | # 指定环境名称 |
多文件配置
可以使用 application-环境名称.yml 指定多环境的配置信息。在主配置文件中,使用 spring.profiles.active 指定当前使用的环境。
可以根据功能对配置文件中的信息进行拆分,,如 application-devDB.yml、application-devRedis 等,之后在主配置文件中引入配置信息,方式有两种:
- 使用
spring.profiles.include引入多个配置,优先级为spring.profiles.active大于spring.profiles.include。 - 使用
spring.profiles.group指定配置组,配置组优先级大于spring.profiles.active。
1 | spring: |